Ultrasound is also known as sonography. It is a medical screening technique that deploys high-frequency sound waves to form real-time images of the inside of the body. It works as a helpful diagnostic tool administered by healthcare professionals to capture image and evaluate a variety of bodily structures and functions. In this guide, we will look into how ultrasound works, its assorted applications, the procedure of undergoing an ultrasound, its safety, restrictions, and the significance it holds in contemporary medicine.
The Process of Ultrasound
Sound Wave Emission: Ultrasound machines release sound waves with frequencies beyond the range of human hearing. These waves are entered into the body to discover internal structures.
Echo Formation: As the ultrasound waves come across different tissues, organs, or fluids within the body, they spring back as echoes.
Image Generation: Specific sensors within the ultrasound probe gather these echoes and transform them into visual images shown on a screen in real time.
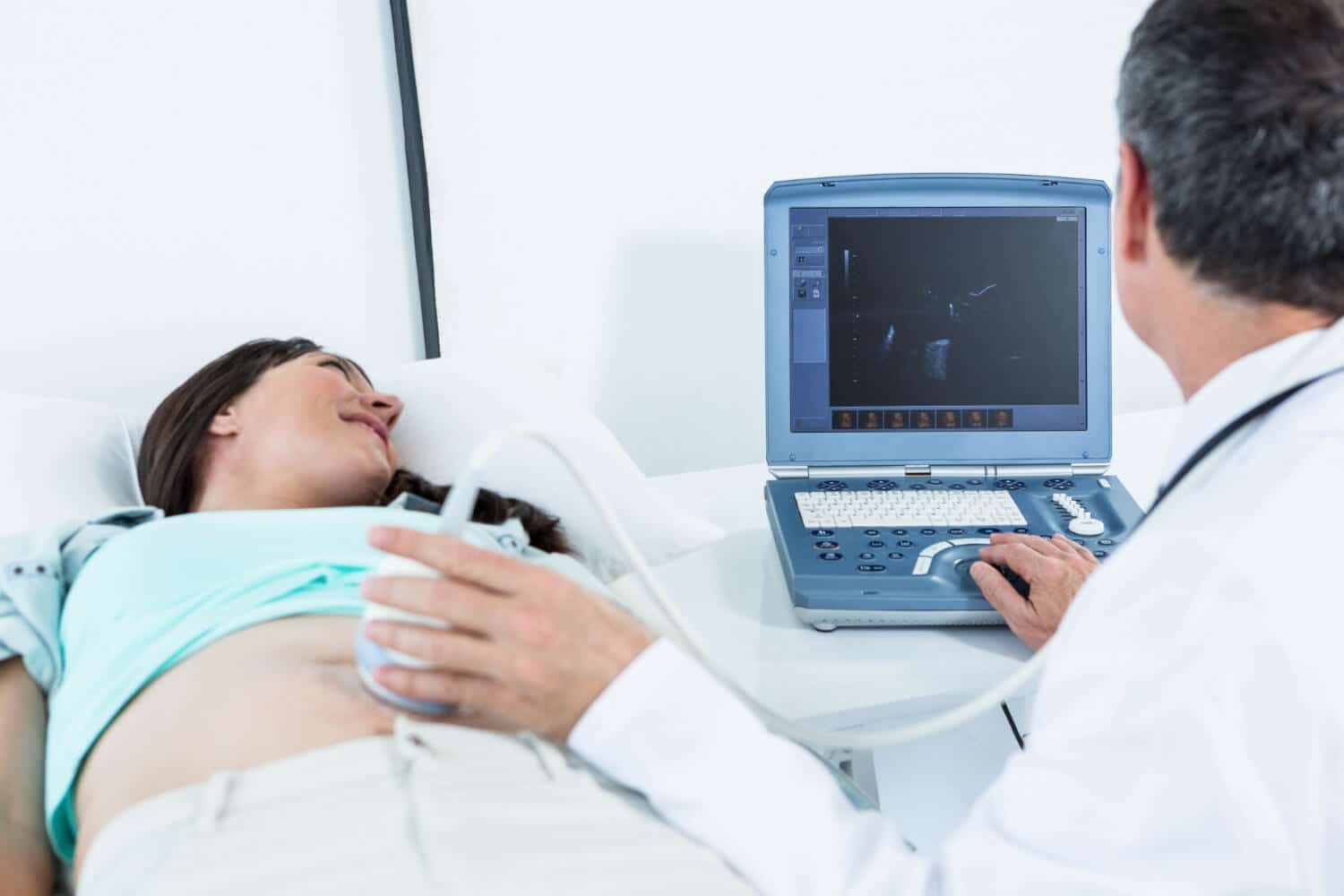
Ultrasound Probe: A handheld tool called an ultrasound probe is moved over the required area to broadcast and receive sound waves. Its movement is proficiently administered by a qualified technician or medical professional.
The Multifaceted Applications of Ultrasound
1- Prenatal Care
Ultrasound plays a crucial role in monitoring the growth of a fetus during pregnancy. It allows healthcare providers to evaluate the baby’s development, placement, and overall health. Ultrasound can discover the baby’s gender if desired by parents.
2- Diagnostic Imaging
Ultrasound is a multipurpose analytic device used to inspect a wide variety of medical conditions. It carries insights into the structure and function of critical organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys, and gallbladder. It identifies the abnormalities, cysts, bumps, tumors, and other concerns.
3- Guidance for Medical Procedures
In diverse medical processes, including biopsies or draining fluid from cysts, Ultrasound is a guiding light for health practitioners. It guarantees precision and curtails the risk of complications.
4- Vascular Assessment
Ultrasound is instrumental in evaluating blood flow within arteries and veins. This is vital for diagnosing conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and evaluating potential blockages.
5- Musculoskeletal Examination
The musculoskeletal system, like muscles, tendons, and joints, can be efficiently examined using Ultrasound. Athletes often go through ultrasound scans to evaluate and monitor sports-related injuries.
6- Breast Health
Ultrasound is executed for spotting and characterizing breast abnormalities and glitches, imperative for breast cancer imaging and diagnosis.
7- Chronic Disease Management
For individuals with long-term disorders like liver cirrhosis, Ultrasound is a helpful tool for ongoing examination of organ health.
What to Expect During an Ultrasound?
Preparation: Depending on the particular type of Ultrasound, you may need to prepare in advance. Such as fasting may be required before an abdominal ultrasound.
Procedure: your healthcare will ask you to position yourself on an examination table, and an experienced technician will apply a gel to the required area. This gel facilitates the conduction of sound waves.
Probe Use: The ultrasound handheld tool is moved over the gel-coated area. Though some weight may be put to get clear images, the process does not cause uneasiness or pain.
Image Monitoring: The technician constantly examines and arranges the ultrasound probe to detain real-time images. They may also take explicit measurements for analysis.
Duration: The time of an ultrasound assessment can be different depending on its purpose, but mostly, it is done within around 30 minutes.
Results: In several cases, you will get instant feedback from the technician. Your radiologist or healthcare provider can interpret the results and provide a complete report.
The Safety of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a safe diagnostic apparatus because it does not emit ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays or CT scans. It is extensively utilized in prenatal care, as it has not been associated with identified risks for pregnant women or developing fetuses. Yet, the frequency and need for ultrasound examinations should be cautiously considered to avoid unnecessary exposure.
Limitations of Ultrasound
While Ultrasound is a valuable medical tool, it comes with certain limitations:
Limited Penetration: Sound waves come across difficulty when penetrating bone and air, which can hamper visualization of some areas within the body.
Operator Skill: The quality of ultrasound images depends on the operator’s expertise in administering the examination.
Patient Factors: Factors including fatness or excess gas in the digestive system can cause challenges in getting clear and precise ultrasound images.
Not Universal: Ultrasound may not be the ideal screening choice for every medical condition, and in some certain cases, other techniques like MRI or CT scans may supply more detailed information.
Ultrasound is a multipurpose, non-invasive, and harmless medical imaging practice that plays a vital role in modern healthcare. From monitoring pregnancies to detecting medical conditions and guiding medical processes, Ultrasound carries out essential insights into the human body’s complications.