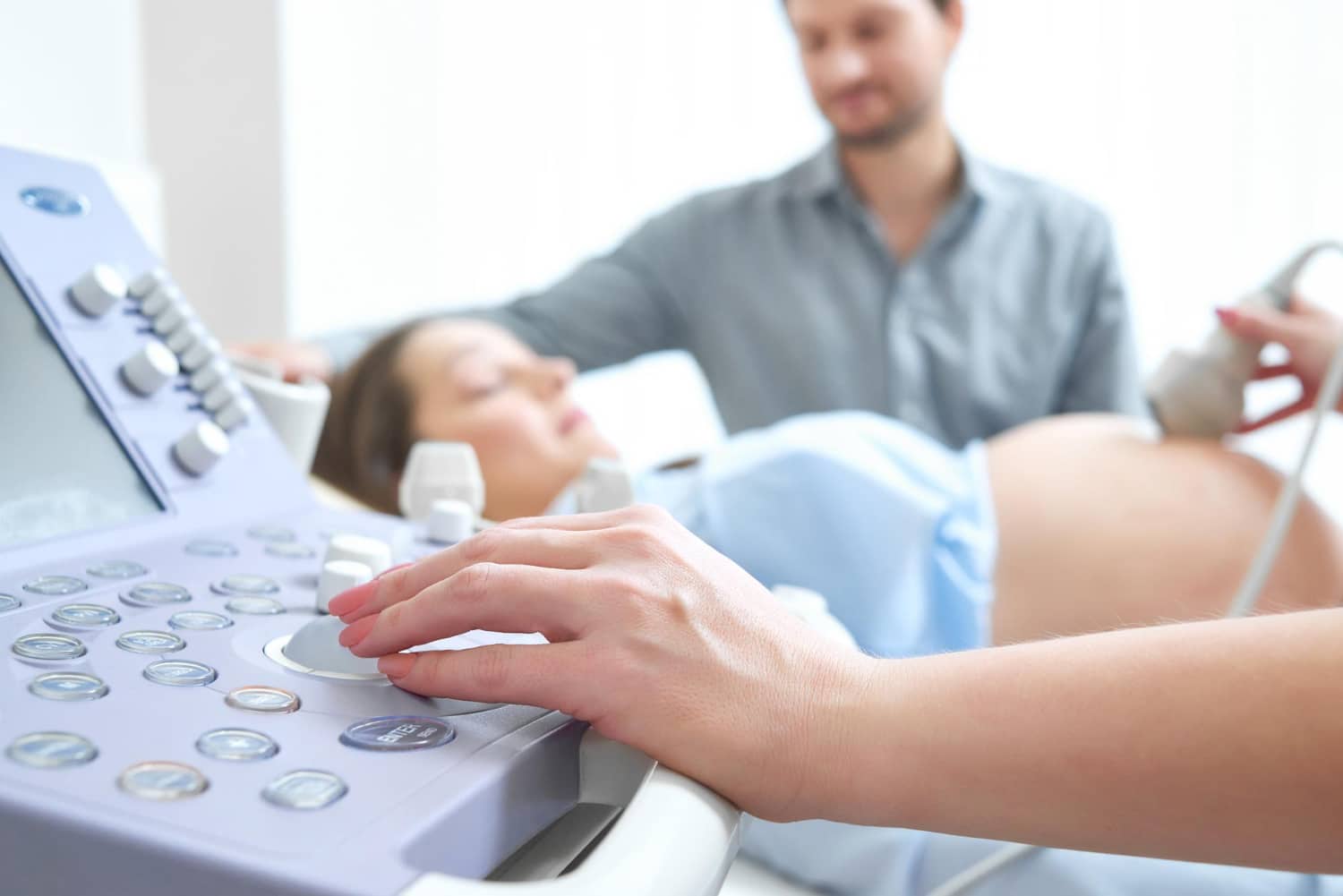
Testing during pregnancy is essential in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions in pregnant women and their babies.
The benefits of testing during pregnancy include the following:
- Providing more accurate information about pregnancy.
- Detecting problems in the fetus or mother earlier.
- Identifying factors that could affect the health of the baby after birth.
- Helping doctors and midwives make decisions about care for mother and baby.
If you have an ultrasound during pregnancy, it can detect any problems with your baby’s organs and make sure everything is developing properly. If there is a problem with one or more organs, you might need additional testing or surgery after birth.
Other tests include blood tests and genetic testing. Blood tests allow doctors to assess how well your body works to eliminate waste byproducts that could harm your growing baby.
What are the Standard Tests that are Performed while having a Pregnancy?
All pregnancies are different, but there are some basic tests that most women can undergo during their pregnancy. These include:
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test or multiple marker test
This blood test measures the level of AFP in your blood and can be performed during any stage of pregnancy. This test helps assess your baby’s health and detect specific congenital disabilities and genetic disorders. AFP is produced by the placenta and your baby’s liver and kidneys, so it can be used to determine how well your baby is growing, what kind of nutritional requirements he has, and whether he may have Down syndrome.
The results of this test can also give you an idea about whether your baby has spina bifida (a condition where there is incomplete closing of the spine), trisomy 21 (also known as Down syndrome), Turner syndrome (an abnormality where one X chromosome is missing or altered), or other genetic abnormalities.
- Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test that can be performed at any point during pregnancy. It’s used to determine whether your baby has certain genetic disorders. The test is done by inserting a needle directly into the amniotic fluid surrounding your baby and then removing a sample of that fluid.
The method works by taking advantage of the fact that amniotic fluid is sterile and contains no bacteria or other harmful organisms. This means that if anything unusual is found in the sample, it’s likely because of something wrong with your baby’s DNA—not because of an infection or other external cause.
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a test performed in the first trimester of pregnancy. It involves using a needle to take a tissue sample from your placenta and testing it for chromosomal abnormalities, like Down syndrome.
CVS is usually done between 10 and 12 weeks into pregnancy and can be done earlier than that if you have a medical reason for doing so. The doctor will insert a small needle through your abdomen into your uterus, then extract some cells from your placenta by drawing them into the syringe. Using this method, they can test for things like Down syndrome, spina bifida, cystic fibrosis, etc.
Once the cells have been extracted from the placenta, they’re sent to a lab to analyze them for genetic abnormalities. If there are any concerns about your baby’s health, you’ll be able to meet with a genetic counselor who will talk with you about all these means and help you decide if additional testing or treatment options are suitable for you.
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing
Cell-free fetal DNA testing is a new method for detecting pregnancies. It’s currently used to screen for fetal chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13.
The method measures the amount of cell-free fetal DNA in the mother’s blood. Fetal DNA is found in the mother’s bloodstream because it crosses the placenta but doesn’t remain there after delivery. The amount of cell-free fetal DNA depends on how many cells are in the fetus at any given time—so if you’re pregnant with twins, there will be more cell-free fetal DNA than if you were pregnant with just one baby.
To perform this test, doctors draw a blood sample early in your pregnancy (around ten weeks). Then they send it to a lab where technicians use molecular biology techniques to look for abnormalities in your DNA that could indicate a chromosomal disorder (or other genetic disorders).
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) is a test performed during pregnancy to determine the condition of the embryo or fetus. It is also used to detect genetic conditions and diseases in the baby.
The test is also known as amniocentesis, which involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid from around the baby in utero. This can be done at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy with no risk to either mother or baby.
A needle is inserted into your abdomen and guided through your amniotic sac to collect a sample of the fluid surrounding your baby. The cells are then analyzed in the lab to check for abnormalities such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, and many others before birth occurs.
- Ultrasound scan
The Prenatal ultrasound scan is a diagnostic test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the internal organs. It’s used during pregnancy to check the baby’s size, position, and development.
It works by sending sound waves through the body and measuring how long it takes to bounce back. The time taken for the sound wave to return reveals details about the structure inside.
Most women have this test around their 12-week or 20-week scan, but it can be done earlier if there are concerns about your or your baby’s health.
Which Ultrasound Scanning Technique is most Effective during Pregnancy?
The ultrasound imaging techniques available to your healthcare provider will depend on the type of ultrasound machine being used, but there are a few more common types.
4-D imaging is similar to 3-D but includes a time dimension that allows the viewer to see how something changes over time. This allows the healthcare provider to see the images’ width, height, and depth as they are being captured. This can be especially helpful when trying to diagnose abnormalities or abnormalities in blood flow patterns.
3-D imaging lets the healthcare provider see an image’s entire width, height, and depth. This can be helpful if it is difficult for your doctor to get an idea of how much tissue is covering something they are looking at.
2D images are taken from one angle and usually only provide a two-dimensional look into what is going on in your body at that moment in time.
Final Word
At Valence Medical Imaging, we understand that every patient is unique and comes with various needs. That’s why we offer a wide range of ultrasound scanning techniques—from traditional to 3D and 4D—to ensure that we can meet all your needs and provide the best care possible.
Our team of expert radiologists can perform non-invasive procedures using state-of-the-art ultrasound technology to help diagnose a wide range of medical conditions. From detecting early signs of cancer to evaluating pregnancies, you can rely on us for accurate results.